The Scrabble Constraint
What is it?
Let w be a word. Define the function S(w) to be the score w would get in a game of Scrabble (assuming no multipliers). Here is a handy image to remind yourself of the scores of each letter in Scrabble:
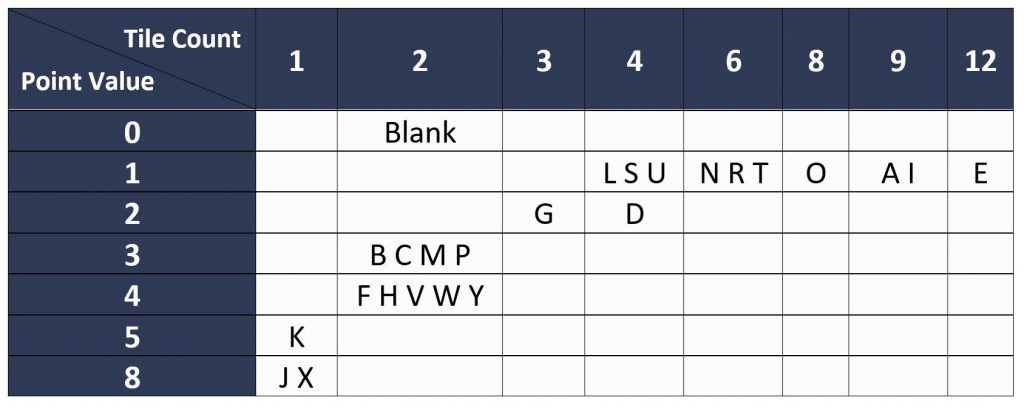
For instance S(SCRABBLE) is 14 and S(SCORE) is 7.
Using this function along with the well-known A1Z26 cipher we can assign each word a letter in the following way:
S(SCRABBLE) = 14 = N
S-invariance
Clearly this string of text doesn't make any sense, and in the vast majority of cases applying this process to a sequence of words will yield no meaning. However, we can now say a body of text is S-invariant if applying the function S to each word leaves the text unchanged.
For instance, the text: "A PRIZE EXAMPLE MODELS EXTRAORDINARILY ODD RAP, SPECIFICALLY A HARDENED SONGWRITING JOB. ACE!" can be converted into the following letters:
Since applying the process to the string of text left it unchanged (albeit shorter), we can call it S-invariant. The factor it was shortened by (90 letters -> 15 letters) can be called it's S-factor. In this case the string of text is S-invariant with an S-factor of 0.166 recurring, or 1/6.
Some theory
Since A has a value of 1 in Scrabble, the word "A" is the shortest S-invariant text, with an S-factor of 1, the highest possible.
It is also immediately obvious that for a string of text to be S-invariant, any subset of words in the text have to also be S-invariant in isolation, including the first word. This means there is only a limited number of words an S-invariant text can start with, listed on Starts. These words have an S-core equal to the A1Z26 value of it's first letter.